
Combination of aptamer and drug for reversible anticoagulation in cardiopulmonary bypass
Gunaratne R, Kumar S, Frederiksen JW, Stayrook S, Lohrmann JL, Perry K, Bompiani KM, Chabata CV, Thalji NK, Ho MD, Arepally G, Camire RM, Krishnaswamy S, Sullenger BA.
Nat Biotechnol. 2018 Aug;36(7):606-613.
The two joint first authors:

Ruwan Gunaratne

Kumar Shekhar
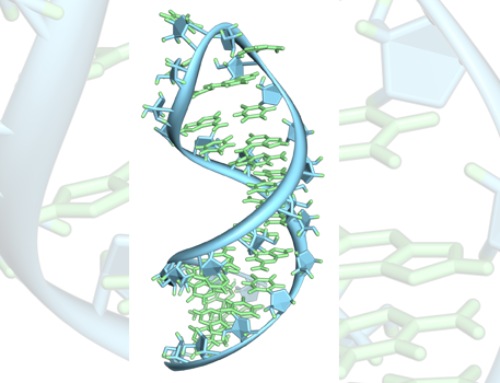
An effective and safer alternative to unfractionated heparin (UFH) for systemic anticoagulation is needed. The Krishnaswamy and Sullenger labs previously showed that the factor Xa (FXa) targeting RNA aptamer 11F7t, though demonstrating substantial anticoagulant effect, was less potent than UFH.
See previous Perspectives On Current Science (here and here) on aptamers or watch an explanation of how aptamers work:
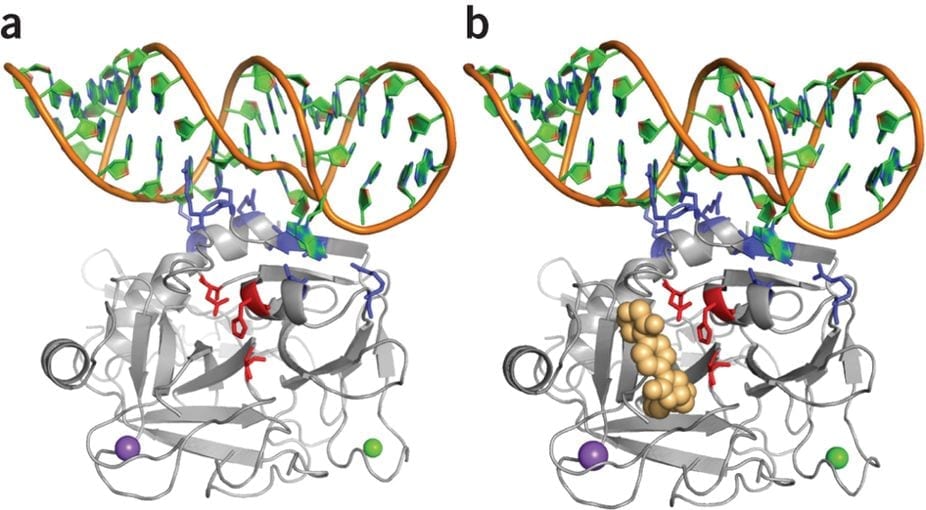
Here, Gunaratne, Kumar and colleagues report on the crystal structures of 11F7t bound to the inactive FXa variant GD-FXaSer195Ala in the presence and absence of the FXa catalytic-site inhibitor rivaroxaban. They show that the aptamer does not occlude the catalytic triad or binding pocket and that there is no structural change between the binary and ternary complex. This suggests that 11F7t and rivaroxaban bind independently and thus inhibit FXa macromolecular interactions and catalytic function with synergistic effects.
An extensive series of experiments confirmed that 11F7t and FXa active-site inhibitors (including apixaban, edoxaban and fondaparinux) did show potentiating synergy. As a result, aptamer/inhibitor combinations can match the anticoagulant potency of UFH. For example, in human blood subjected to more than 2h of continuous extracorporeal circulation aptamer/FXa inhibitor combinations were more effective than UFH in limiting thrombin generation. In contrast to UFH, 11F7t alone or in combination with active-site inhibitors did not induce platelet aggregation in the blood from patients suffering heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
Additionally, the catalytically inactive FXa decoy protein GD-FXaSer195Ala effectively neutralized the inhibitory effects of the aptamer/apixaban combination while the sequence specific complementary oligonucleotide AO5-2 could only partially reverse the effects.
Why you should read it
The use of aptamers targeting exo-sites in combination with existing catalytic-site directed small molecule drugs may be a generalized approach for identifying potent combinatorial therapies in a variety of clinical contexts.