
RNA inhibitors of nuclear proteins responsible for multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
Urak KT, Blanco GN, Shubham S, Lin LH, Dassie JP, Thiel WH, Chen Y, Sonkar VK, Lei B, Murthy S, Gutierrez WR, Wilson ME, Stiber JA, Klesney-Tait J, Dayal S, Miller FJ Jr, Giangrande PH.
Nat Commun. 2019 Jan 10;10(1):116.
The three joint first authors:

Kevin T. Urak

Giselle N. Blanco

Shambhavi Shubham
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome(MODS) is a clinical complication caused by severe trauma or cytotoxic insult with a 45% mortality rate. To date, there is no approved treatment or widely accepted explanation for the pathogenesis of MODS, though recently, extracellular histones have been implicated as mediators. In this paper, Urak, Blanco, Shubham and colleagues demonstrate that aptamers selected against human histones H3 and H4 ameliorate a number of pathological features and prevent death in a mouse model of MODS.
For an in-depth discussion of MODS please see:
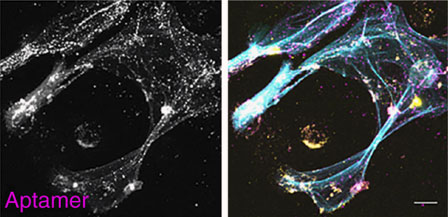
The authors first isolated highly specific 2′ fluoro-modified aptamers with 1-5 nM affinity to H3 and H4 using SELEX that included negative selection against bovine serum albumin (BSA) and human IgG. The two lead candidates, KU7 and KU9, were cross-reactive with calf thymus-derived histones (CTH) as well as human histone H1 and showed extended half-life in 50% human serum (KU7 150 h; KU9 48 h). When incubated with human platelets, KU7 and KU9 inhibited histone H4- but not collagen-induced platelet aggregation. Similarly, KU7 and KU9 inhibited histone- but not lipopolysaccharide-induced TLR activation. The anti-histone aptamers also protected human hybrid endothelial cells from the cytotoxic effects and increased calcium influx caused by CTH administration.
In a mouse model of MODS, the aptamers completely prevented death resulting from histone injection and partially normalized the increase in platelet numbers and TLR activation in the liver. These effects were retained to a large degree even with delayed administration of the aptamers after histone insult (up to 120 min in vitro and 30 min in vivo). Importantly, Ku7 co-localized with histones in neutrophil extracellular traps(NETs) generated from PMA-stimulated human neutrophils and inhibited NET-induced cell death. NETs have previously been described as a source of extracellular histones in a variety of clinical disease such as sepsis, rheumatologic diseases and thrombosis.

Prof. Francis J. Miller

Prof. Paloma H. Giangrande
Why you should read it
The success of the anti-histone RNA aptamers described here supports their clinical development not only for MODS but other conditions which have been linked to the toxic effects of extracellular histones.